Employees aware of the company’s strategy are expected to make better choices daily. Their actions are more aligned with the company’s course. Learn how to measure strategy awareness KPI.
Research shows that 95% of a company’s employees are unaware of the company’s strategy. What do we mean by “strategy awareness” in this case? Why is it important? How to measure and improve it?
Key topics:
- What is Strategy Awareness Level?
- Why do we Need to Measure Strategy Awareness?
- What We Mean by an Employee Who is Aware of the Strategy
- Measuring Strategy Awareness
- An Example of Measuring Strategy Awareness Level
- Algorithm to Measure Strategy Awareness
What is Strategy Awareness Level?
Strategy awareness level is a percent of employees who are “aware of the strategy”.
The starting formula is this one:
Strategy awareness level = (Employees aware of the strategy / Number of FTE) * 100%
Where FTE refers to Full-Time Equivalent Employee.
While the formula looks simple, we still need to:
- (a) Define what we mean by “an employee who is aware of the strategy.”
- (b) Find the cost-effective way to count the number of those employees.
Why do we Need to Measure Strategy Awareness?
There are many reasons, for example, strategy awareness is one of the leading factors of high employee engagement; it also helps to address the strategy execution gap.
I see the ultimate purpose of measurement in the following way:
We want our employees to understand strategy to the degree needed to help them make the right decisions without direct control of managers.
What We Mean by an Employee Who is Aware of the Strategy
In the formula for “Strategy awareness level,” we have “Employees aware of the strategy.” What do we mean by this?
Here we have several ideas to consider:
- Employee who knows that strategy exists.
- Employee who knows how the strategy is formulated.
- Employee who understands how strategy affects the choices that he/she does daily.
Let’s test these options against the purpose of measurement formulated above. The first two options don’t help us much with daily choices, so option (3) is the only applicable.
Having said that, we can make two conclusions:
Conclusion 1:
It makes sense measuring awareness level of strategy in application to some specific domain only.
otherwise:
Conclusion 2:
When we measure strategy awareness in general, we will simply push employers towards memorizing right words.
Good Strategy Comes First
Before moving ahead with measuring strategy awareness level, I’d like to introduce another important principle:
Strategy comes first:
It is impossible to measure awareness level for the strategy when the strategy itself is not well-formulated.
The reason is that we simply won’t be able to validate accurately the activities of the employees.
Before trying to measure strategy awareness, we have to make sure that the strategy itself exists and is well-described.
Here are the signs of a well-formulated strategy, most of them are covered by K&N Balanced Scorecard:
- Plain English used (no business jargon, no uncommon abbreviations, no buzzwords).
- There is a strategy map where the cause-and-effect logic can be tracked.
- The goals have action plans or hypothesis to test.
- There is supporting documentation that explains the rationale behind the goals.
- The goals are quantified with KPIs.
If your strategy passed this checklist, then go to the strategy awareness measurement step.
Measuring Strategy Awareness
We are interested in the practical application of strategy awareness. Our goal is to find out if employees know strategy to the degree that helps them with their daily decision making.
How can we measure this type of strategy awareness?
Measure the changes in action:
The best way to measure the awareness about something is actually measuring the changes in actions that it implies.
Strategy Awareness for Known Challenges
Think about safety awareness training. It might have 100% attendance rate, trainees might even pass all exam tests, but what ultimately matters is that the training has an effect on their daily routines in the sense of increased safety (here are some examples of specific safety KPIs).
For known challenges:
Strategy awareness for the known challenges can be quantified by the expected changes in the behaviour
See the example of customer support specialist below.
Strategy Awareness for Unknown Challenges
What about the cases when we cannot measure an impact of strategy awareness on specific behaviour? I this case, we need to find some proxy for strategy awareness.
Proxy for the strategy awareness:
The best proxy for the strategy awareness is strategy alignment, e.g, when the goals of the individuals are aligned with overall strategic goals
Think about a software engineer. Due to the nature of his/her job, we cannot quantify specific signals of behaviour change due to strategy awareness, but we can use frameworks such as OKR to make sure that the goals of the engineer are aligned with the company’s strategy.
- In this case strategic alignment is a perfect confirmation of the strategy awareness.
An Example of Measuring Strategy Awareness Level
We agreed to measure the strategy awareness level in the context of a specific business domain.
Stakeholders
- This implies that we need to focus on certain stakeholders.
I’m not suggesting to build information silos, but it is a good idea to explain and adapt strategy according to the needs of stakeholders who will follow it.
Let’s see how the strategy awareness level can be measured in a case of customer support specialists.
Strategy
What piece of strategy should a customer support specialist be aware of?
- The main challenges in this case will be related to effective access to the information and tools needed to address customer queries (you can find an example of strategy map for a customer service here).
- A customer support specialist should also be aware of quality and learning aspects of strategy. For example, being able to collect and report near-miss issues or support a company’s strategy in listening to customers better.
Measurement
If we want to understand a strategy awareness level, in this case, we can look at:
- How effective is a customer specialist in reporting those near-miss cases?
and
- How many improvement ideas were noted down by a specialist as a result of the conversations with customers?
For example, we can say that an employee is aware about strategy when
- He/she reported at least 1 near-miss incident within the last month
and
- Shared at least 2 improvement ideas within the 3 month period.
The benchmarks here should be on a minimal level as we are not trying to validate the employees´ skills (even if that was the case, more doesn’t necessarily mean better in the case of near-miss reporting).
Not Doing Equals Not Knowing
What about those cases when an employee is aware about, for example, near-miss reporting but doesn´t report accordingly?
Not doing equals not knowing
If you prefer some more detailed interpretation, I’d say that the absence of action is a sign of low/false awareness about the topic. For example, the person might know about the formal need to report near-miss, but did not have enough training/leadership to establish the right behaviour patterns.
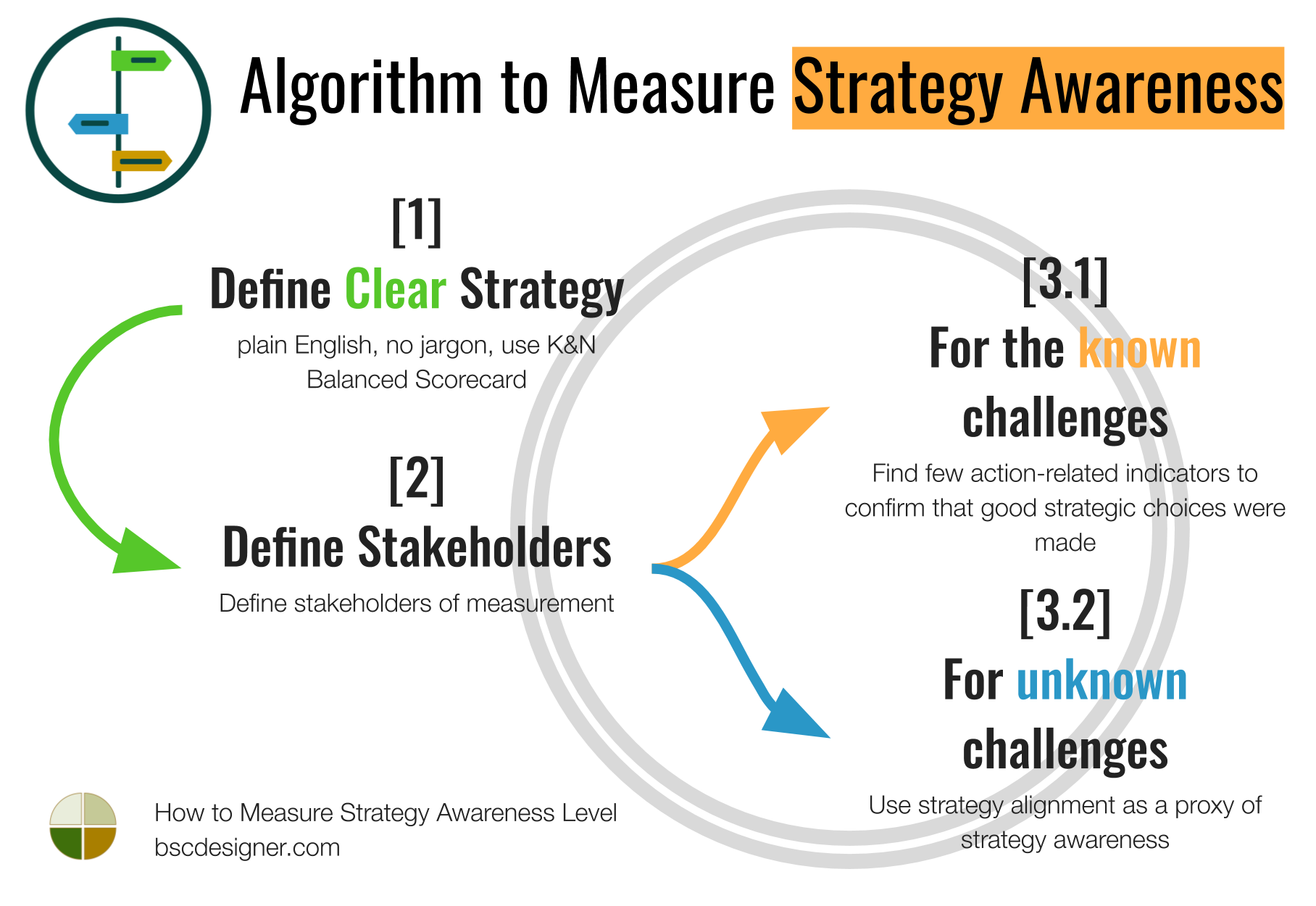
Algorithm to Measure Strategy Awareness
Let’s formulate the main takeaways of this article in the form of strategy awareness measurement algorithm:
- Define clear strategy (plain English, no jargon, use K&N Balanced Scorecard).
- Define stakeholders of measurement.
- For the known challenges (like customer support in the example above): find few action-related indicators to confirm that good strategic choices were made.
- For unknown challenges (like software engineer in the example above): use strategy alignment as a proxy of strategy awareness (OKR framework).
Questions? Ideas? Feel free to share in the comments.
BSC Designer is strategy execution software that enhances strategy formulation and execution through tangible KPIs. Our proprietary strategy implementation system reflects our practical experience in the strategy domain.